
Prophase 2:No recombination can be identified during prophase 2. Prophase 1:Genetic material is exchanged by crossing over leads to the recombination during the prophase 1. Prophase 2: No crossovers and chiasmata formation is identified in prophase 2. Prophase 1:Occurrence of crossovers and the formation of chiasmata takes place during prophase 1. Prophase 2: During prophase 2, the spindle apparatus is arranged in a plane which is rotated by 90º relative to the meiosis 1. Prophase 1: During prophase 1, the spindle apparatus begins to form in the cell equator.

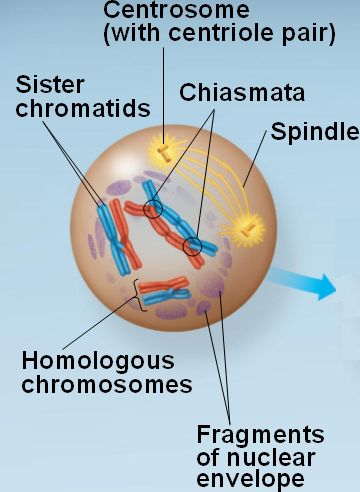
Prophase 2: Prophase 2 occurs in haploid cells. Prophase 1: Prophase 1 occurs in diploid cells. Prophase 2: Individual chromosomes are involved in the prophase 2. Prophase 1: Homologous chromosomes are involved in the prophase 1. Prophase 2: Centrosome is duplicated during the prophase 2 due to the lack of an interphase prior to the prophase 2. Prophase 1:Centrosome is duplicated during the interphase, which is a process prior to prophase 1. Prophase 2: No interphase takes place before prophase 2. Prophase 1: Prophase 1 follows a long interphase. Prophase 2: Meiosis 2 begins with prophase 2. Prophase 1: Meiosis 1 begins with prophase 1. The cross-over occurs at a chiasma, leading to the exchange of chromosomal parts.įigure 2: Phases of Meiosis Difference Between Prophase 1 and 2 Meiosis The two homologous chromosomes are separately shown in red and green colors. A chiasma is a point where the homologous chromosomes are in contact. During the synapsis, non-sister chromatids are allowed to cross-over at their chiasmata. Homologous chromosome pairing, which is known as synapsis, is a critical step in meiosis, in order to obtain a proper segregation of chromosome sets between two daughter cells.

These bivalents pairs form tetrads with other homologues during the prophase 1. These replicated chromosomes are called bivalents. In order to enter a cell into the meiotic division, chromosomes in the vegetative germ cell should be replicated. Chromosomal crossover occurs during prophase 1, leading to genetic variations by recombination. It is considered as the longest phase of the whole meiosis. Prophase 1 is the initial phase of the meiosis 1. What is the difference between Prophase 1 and 2 The main difference between prophase 1 and 2 is that genetic recombination occurs through crossing overs and the “Chiasmata” formation during prophase 1 whereas no genetic recombination is noticed at the prophase 2.ģ. Diploid germ cells undergo the above mentioned two stages of meiosis in order to produce their haploid gametes. Prophase 1 is the initial phase of meiosis 1 and prophase 2 is the initial phase of meiosis 2. Two stages of meiosis can be identified, meiosis 1 and meiosis 2. Prophase 1 and 2 are two phases in the meiotic division of cells which produce gametes in order to carry out their sexual reproduction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
